Weight Loss and Health
Overweight and obesity are major ongoing health issues in US adults and children, whose prevalence will continue to increase. Obesity at any age can increase your risk for other health complications in the future such as diabetes, cardiovascular issues, sleep apnea, gallbladder disease, etc. The definition of an overweight adult is someone having a BMI (body mass index) of >25, while obesity can be defined as someone who has a BMI>30. The definition of an overweight child is BMI at or above 85th percentile but below 95th percentile on CDC growth chart, while obesity can be defined as BMI of the 95th percentile on CDC growth chart. Fat cell numbers increase when energy in exceeds energy out.
There are two types of obesity/ways to store excess fat:
- Hyperplastic obesity: is the obesity due to an increase in the number of fat cells- people with this tend to regain lost weight back rapidly.
- Hypertropic obesity: is the obesity related to an increase in the size of the fat cells.
People with an average number of fat cells may be more successful at maintaining weight loss.


Obesity or excess fat is caused by:
- Genetics
- Environment
- Culture
- Behavior
Dangerous weight loss Interventions such as fad diets, diet books, severe/quick weight-loss programs with non-credentialed clinicians are not sustainable and leave people feeling discouraged and even gaining all the weight back and more.
Successful weight loss strategies include reasonable goals, small changes, and moderate wt loss, nutrition counseling, and motivational interview counseling.
Medical Nutrition Therapy for People with Diabetes
What exactly is diabetes?
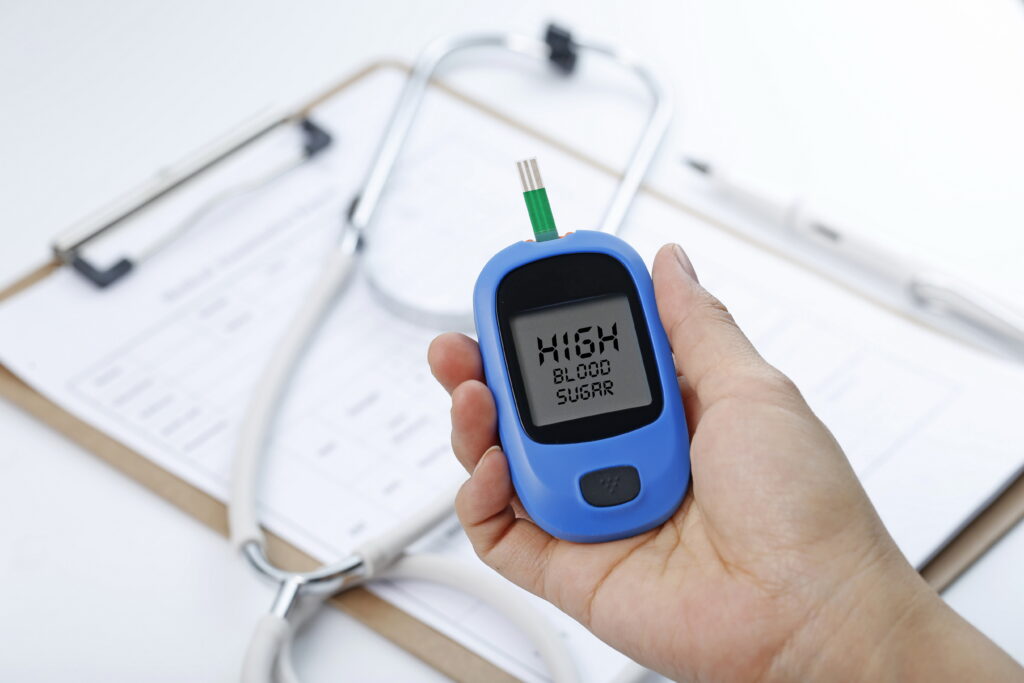
In general diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. High blood sugar problems start when your body no longer makes enough of a hormone called insulin.
Your body changes much of the food you eat into a type of sugar called glucose. This sugar travels in your blood to all the cells in your body. Your body cells need the sugar to give you energy.
Insulin helps sugar move from your blood into your cells. Without insulin, your cells cannot get the sugar they need to keep you healthy.
By moving sugar from your blood to your body’s cells, insulin helps keep your blood sugar level within normal limits. When you don’t have enough insulin to lower high blood sugar levels, you are diagnosed with diabetes.
There are two different types of diabetes, type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes means your body does not make enough insulin. This can develop at any age and in adults accounts for 5% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes. Type 2 diabetes means your body cannot use insulin properly and can also develop at any age. This accounts for 95% of all adult cases of diabetes.
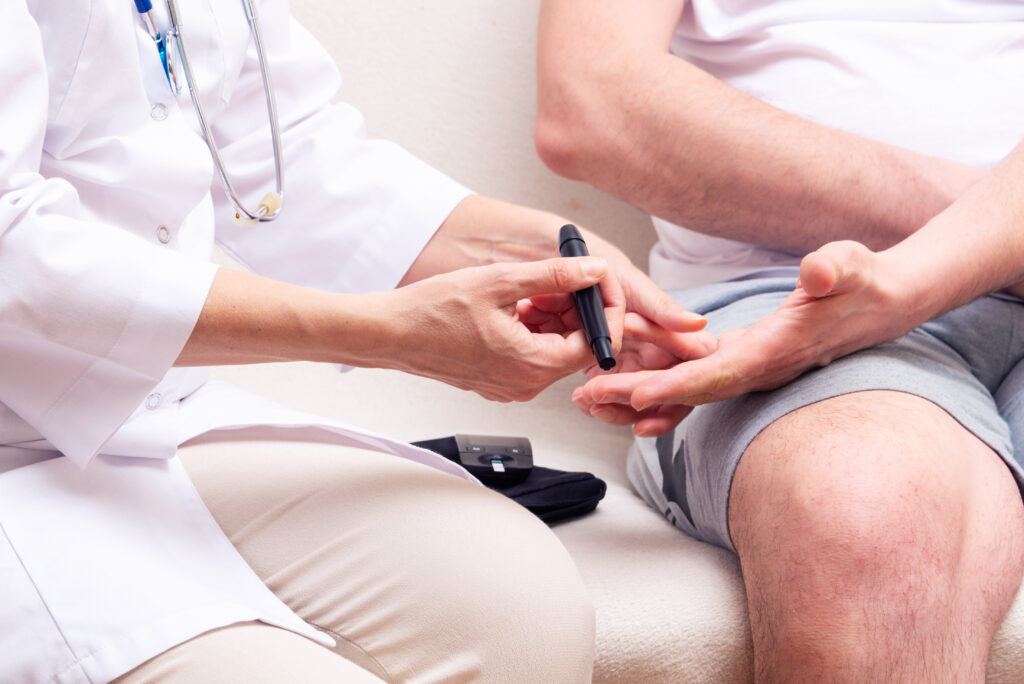
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes:
- Have a family history
- Being physically inactive over a long period of time
- Being 45 years of age and older
- Being overweight
How can you manage your diabetes?
- Working with a health professional such as a Registered Dietitian to manage your diabetes in the most sustainable way for your lifestyle.
- Learning about a healthy diet that is individualized for you.
- Coming up with an activity schedule.
- Weight loss.